Here are old articles about OpenConnect, the open source AnyConnect server: OpenConnect on Ubuntu Open Connect Server Configuration (Working for iOS) Cisco AnyConnect Client for OS X/Windows/Linux (Version 3.1.05160) This time, OCServ 0.80 on Ubuntu 14.04. And still doesn’t work for OS X.
- An openconnect VPN server (ocserv), which implements an improved version of the Cisco AnyConnect protocol, has also been written. OpenConnect is released under the GNU Lesser Public License, version 2.1.
- I too have the same problem. Changing the metric did not work. As soon as i connect to Cisco VPN, WSL2 looses connectivity to the internet as well connectivity to the host via WSL network adapter. Ping using loopback IPs 127.0.1.1 works but not via the virtual ethernet adapters.
- The program openconnect connects to VPN servers which use standard TLS/SSL, DTLS, and ESP protocols for data transport.
- I needed to maintain a continuous (or near-continuous) VPN connection to a server (server 1) from another server (server 2) that was running a Tomcat web-app (on Ubuntu Server 16.04). Server 1 was part of a network which provides secured VPN access to external connections via Cisco Anyconnect.
Links for openconnect
Ubuntu Resources:
Cisco Anyconnect For Ubuntu
Download Source Package openconnect:
Maintainer:
- Ubuntu MOTU Developers (Mail Archive)
Please consider filing a bug or asking a question via Launchpad before contacting the maintainer directly.
Original Maintainers (usually from Debian):
- Mike Miller
- Luca Boccassi
It should generally not be necessary for users to contact the original maintainer.
External Resources:
- Homepage [www.infradead.org]

Similar packages:
open client for Cisco AnyConnect, Pulse, GlobalProtect VPN
Other Packages Related to openconnect
|
|
|
|
- dep:libc6 (>= 2.14) [amd64]
- GNU C Library: Shared libraries
also a virtual package provided by libc6-udeb
- dep:libc6 (>= 2.17) [arm64, ppc64el]
- dep:libc6 (>= 2.8) [armhf, s390x]
- dep:libgnutls30 (>= 3.6.5)
- GNU TLS library - main runtime library
- dep:libopenconnect5 (>= 8.01)
- open client for Cisco AnyConnect, Pulse, GlobalProtect VPN - shared library
- dep:libproxy1v5 (>= 0.4.14)
- automatic proxy configuration management library (shared)
- dep:libxml2 (>= 2.7.4)
- GNOME XML library
- dep:vpnc-scripts
- Network configuration scripts for VPNC and OpenConnect
Download openconnect
| Architecture | Package Size | Installed Size | Files |
|---|---|---|---|
| amd64 | 452.8 kB | 2,686.0 kB | [list of files] |
| arm64 | 451.4 kB | 2,682.0 kB | [list of files] |
| armhf | 450.8 kB | 2,665.0 kB | [list of files] |
| ppc64el | 454.8 kB | 2,754.0 kB | [list of files] |
| s390x | 451.6 kB | 2,682.0 kB | [list of files] |
Problem
I needed to maintain a continuous (or near-continuous) VPN connection to a server (server 1) from another server (server 2) that was running a Tomcat web-app (on Ubuntu Server 16.04). Server 1 was part of a network which provides secured VPN access to external connections via Cisco Anyconnect.
Solution
Users have reported that this approach does not work with newer version of openconnect etc.
Given I haven't attempted this approach (nor have need of it) I am just leaving this here for historical purposes (or something that did work previously).
For this, we're going to use the excellent OpenConnect to connect to server 1, and a bash script to continuously check the connection, and if disconnected, to reconnect.
Install OpenConnect
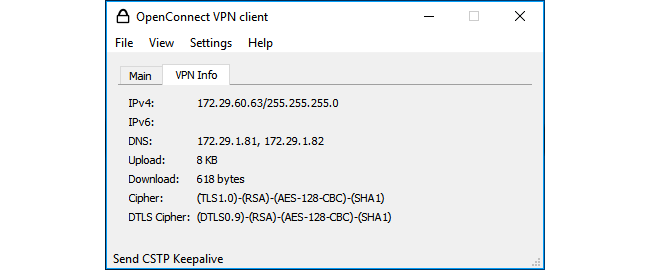
Let's first install OpenConnect. Server 2 was running Ubuntu 16.04. Let's do:
Creating a script to reconnect when disconnected
Please note that the below approach stores a vpn password in clear text in the script file, and as such is a potential security risk. The script should be locked down to stop users without authorisation from viewing its contents. Hence, this approach may only be appropriate for a server/system that is strictly managed or not accessed by other users.
Let's create a script that will:
- connect to your VPN;
- check every
xseconds whether it is still connected - reconnect to the VPN if the connection is broken
In the below example we'll create a vpn.sh script.
Copy the following into in your script:
Let's at least lock this file down to be only readable by root:
Running script in background
Once your happy with your script you can run said script as a background script:
Stopping background script
To stop/disconnect the VPN and script, use ps to find the PID's of the VPN script and the openconnect process by:
For example, on my system, running the above gives:
I would kill PID's 10525 and 28445, like this:
Split tunnelling with vpn-slice
Split tunnelling allows you to explicitly define the ip address(es) for which traffic will be routed to on the vpn server side. This is useful for situations where you might want to route traffic to/from a specific ip, and want all other traffic to use normal (non-vpn) connections.
For this use case you can use vpn-slice. Once installed (see here for requirements and install guide), you can then modify your the script above as follows (see line 15 for the vpn-slice script argument):
where <IP-ADDRESS> is the ip address (or addresses, separated by a space) is what addresses you want tunnelled to the vpn.
NOTE: you should install vpn-slice with sudo to ensure it is available on the standard path (otherwise you'll need to give the full path to the vpn-slice script).
References
Cisco Anyconnect For Linux Ubuntu
Related articles
Ubuntu Openconnect Cisco Anyconnect Windows 10
- Page:
